Linux 静态链接和动态链接
C程序编译过程
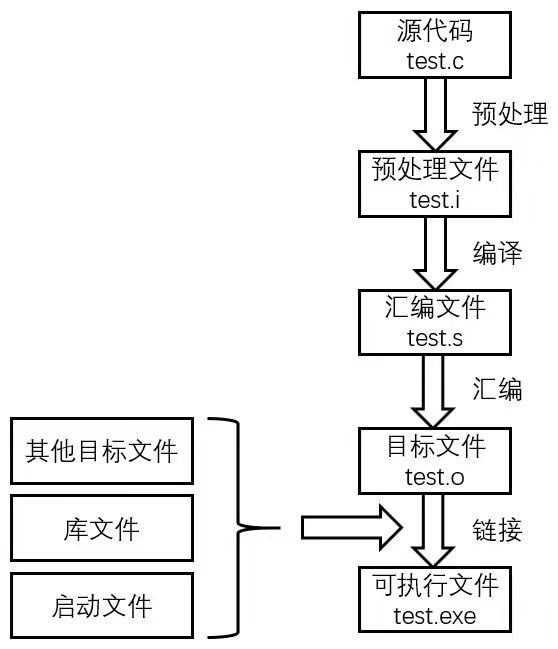
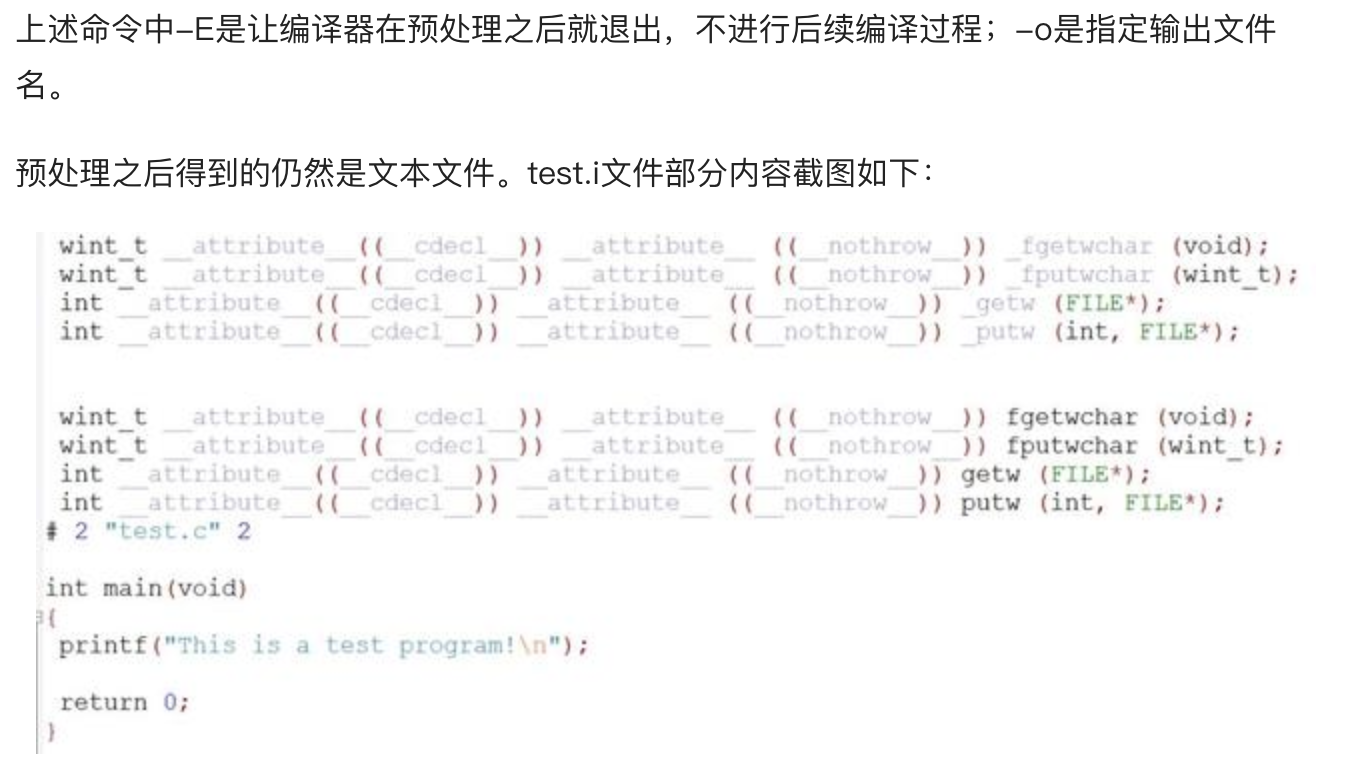
1.预处理(Preprpcessing)
使用预处理器把源文件test.c经过预处理生成test.i文件,预处理用于将所有的#include头文件以及宏定义替换成其真正的内容。
gcc -E test.c -o test.i
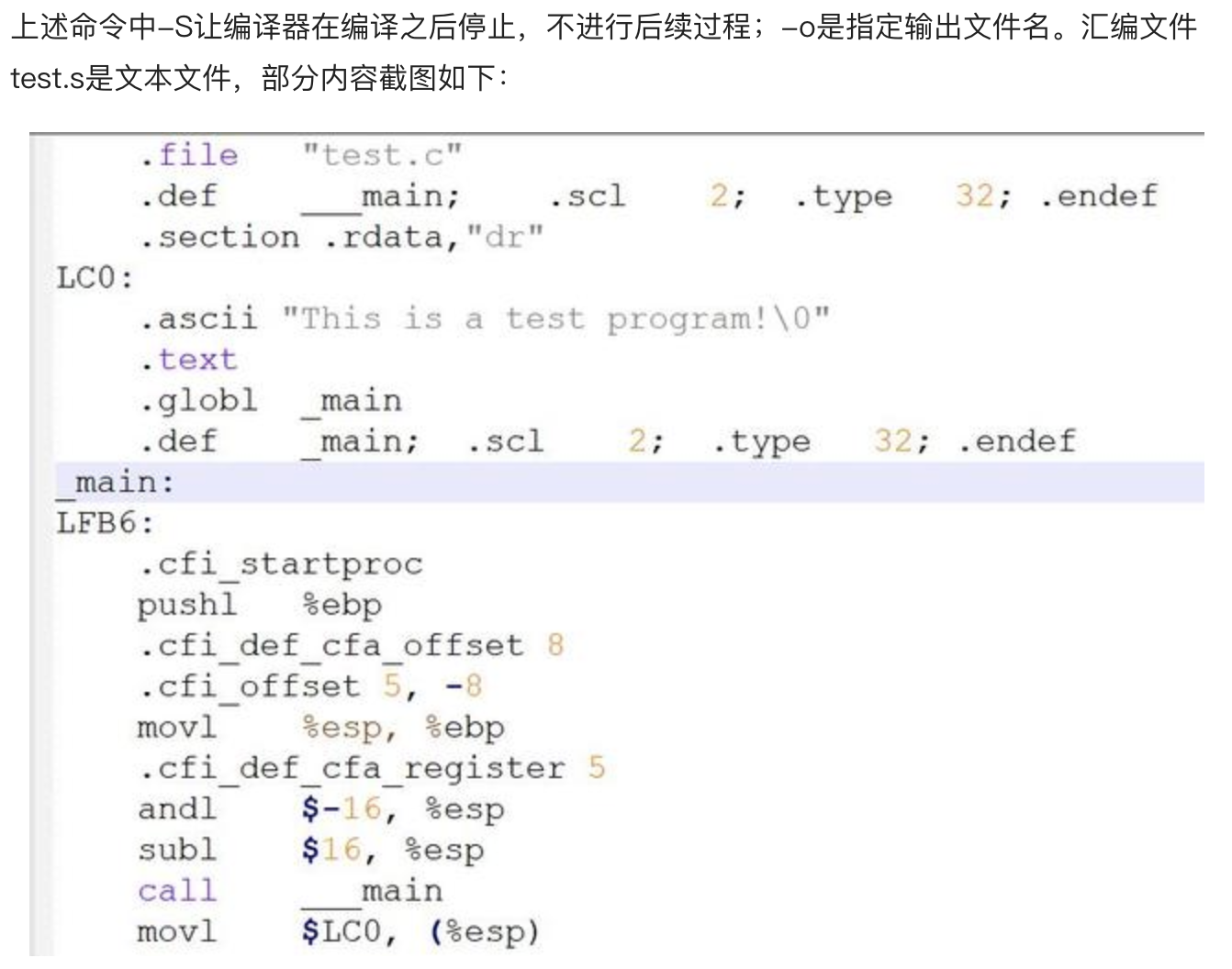
2.编译(Compilation)
使用编译器将预处理文件test.i编译成汇编文件test.s。
gcc -S test.i -o test.s
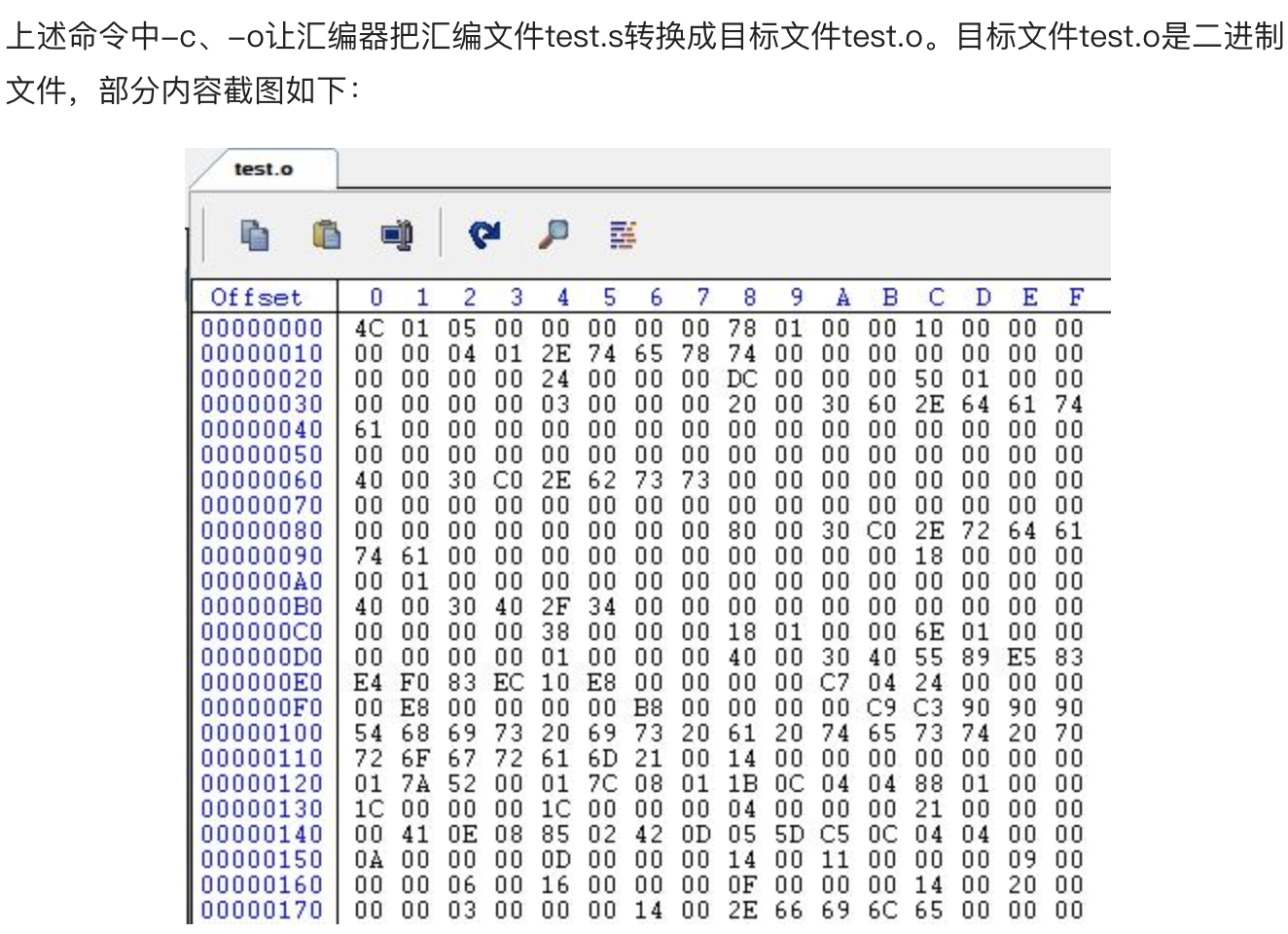
3.汇编(Assemble)
使用汇编器将汇编文件test.s转换成目标文件test.o。
gcc -c test.s -o test.o
4.链接(Linking)
链接过程使用链接器将该目标文件与其他目标文件、库文件、启动文件等链接起来生成可执行文件。
gcc test.o -o test.exe
静态、动态链接?
- 1、什么是静态链接?
静态链接是由链接器在链接时将库的内容加入到可执行程序中的做法。链接器是一个独立程序,将一个或多个库或目标文件(先前由编译器或汇编器生成)链接到一块生成可执行程序。这里的库指的是静态链接库,Windows下以.lib为后缀,Linux下以.a为后缀。
- 2、什么是动态链接?
动态链接(Dynamic Linking),把链接这个过程推迟到了运行时再进行,在可执行文件装载时或运行时,由操作系统的装载程序加载库。这里的库指的是动态链接库,Windows下以.dll为后缀,Linux下以.so为后缀。值得一提的是,在Windows下的动态链接也可以用到.lib为后缀的文件,但这里的.lib文件叫做导入库,是由.dll文件生成的。
实验
文件1(main.c):
#include "test.h"
int main(void)
{
print_hello();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
文件2(test.c):
#include "test.h"
void print_hello(void)
{
printf("hello world\n");
}
文件3(test.h):
#ifndef __TEST_H
#define __TEST_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void print_hello(void);
#endif
静态链接实验
-
编译
gcc -c test.c main.c多出了test.o和main.o文件
-
静态链接库
接下来使用ar工具把test.o和main.o打包成一个静态库文件lib_test.libar rv lib_test.lib test.o main.o -
链接
把这个静态库链接成可执行文件lib_test.exegcc lib_test.lib -o lib_test.exe
可以直接执行lib_test.exe
动态链接实验
-
动态链接库
gcc test.c -shared -o dll_test.dll多出了动态库文件dll_test.dll -
生成可执行文件
用该动态库文件dll_test.dll与main.c一起编译生成可执行文件dll_test.exegcc dll_test.dll main.c -o dll_test.exe